It’s hard to believe, but the SRT open source protocol is celebrating its four-year anniversary this month. To mark this milestone, we’ve put together this comprehensive guide to everything you need to know about the video streaming protocol that’s completely disrupted the way the world streams video. In this blog post, we’ll explore the benefits of SRT, how it works, who uses it, and how it powers Haivision solutions.
- What is SRT?
- A Brief History of SRT
- How Does SRT Work?
- Benefits of SRT
- How Does SRT Compare to Other Protocols?
- What is the SRT Alliance?
- Who Uses SRT?
- Success Stories: SRT Trailblazers
- Haivision Solutions Powered by SRT
What is SRT?
SRT is a video streaming transport protocol and technology stack designed to connect two endpoints for the purposes of delivering low latency video and other media streams across lossy networks such as the public internet. In a nutshell, SRT brings the best quality live video over the worst networks. It accounts for packet loss, jitter, and fluctuating bandwidth all while maintaining the integrity and quality of video. With SRT, you can keep your streams secure and easily traverse firewalls.
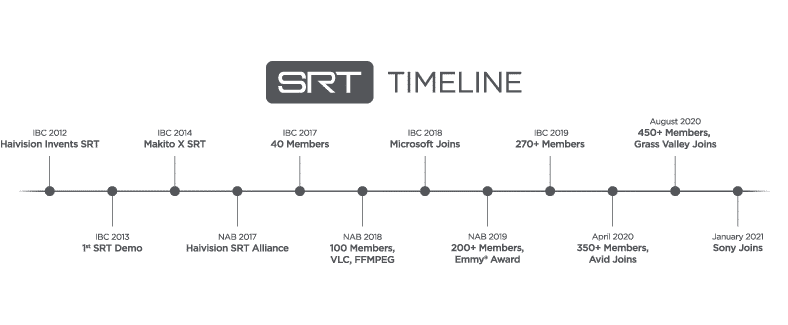
A Brief History of SRT
Born from the need to reduce the high cost of contribution by satellite and private networks, SRT was originally developed and pioneered by Haivision. It was publicly demonstrated for the first time at IBC 2013, and, as the technology progressed, Haivision released SRT as part of its product family and customers started to enjoy the benefits of high-quality, low latency secure video over unreliable public networks.
To encourage widespread adoption so that more companies and customers could benefit from this exciting technology, Haivision released SRT on GitHub in 2017 as an open source technology stack and protocol. Since then, support for the protocol has continued to grow from strength to strength and in 2018 Haivsion was awarded an Emmy® Award by the NATAS Technology & Engineering Achievement Committee for pioneering a reliable transmission method for live contribution and distribution TV links.
“We’re excited about SRT…it’s enabling us to provide rock-solid services, you never lose a piece of video, you always get video to screen but starting to work at different price points because we’re using internet rather than traditional fixed networks as a way of carrying streams.”
Steve Russell, Head of OTT & Media Management Portfolios, Red Bee Media
How Does SRT Work?
SRT solves the latency challenges of live video transport that persist despite advances in internet streaming, such as packet loss, jitter, and bandwidth limitations. SRT provides a secure and reliable solution for low latency video transport and includes:
- End-to-end security with AES 128/256-bit encryption
- Packet loss recovery through advanced low latency retransmission techniques
- Video and audio stream timing recovery
- Simplified firewall traversal
- Network health monitoring between endpoints (packet loss, latency, jitter)
For a simple explanation of what SRT does, and how it works, watch our SRT 101 video.
Benefits of SRT
Although sometimes dubbed as “Satellite Replacement Technology”, SRT has so much to more to offer, including:
- Pristine Quality
SRT protects against jitter, packet loss, and bandwidth fluctuation, ensuring the best possible viewing experience. - Extremely Secure
Using the same 128/256-bit AES encryption trusted by governments and organizations around the world, SRT ensures that valuable content is protected end-to-end from contribution to distribution so that no unauthorized parties can listen. - Always Reliable
No matter how unreliable your network, SRT can recover from severe packet loss and jitter, ensuring the integrity and quality of your video streams. - Low Latency
SRT’s stream error correction is configurable to accommodate a user’s deployment conditions. Leveraging real-time IP communications development to extend traditional network error recovery practices, SRT delivers media with significantly lower latency than TCP/IP, while offering the speed of unreliable UDP transmission without the disadvantage - Easy Firewall Traversal
The handshaking process used by SRT supports outbound connections without the potential risks and dangers of permanent exterior ports being opened in a firewall, thereby maintaining corporate LAN security policies and minimizing the need for IT intervention. - Content Agnostic
Unlike some other streaming protocols that only support specific video and audio formats, SRT is payload agnostic. Because SRT operates at the network transport level, acting as a wrapper around your content, it can transport any type of video format, codec, resolution, or frame rate. - Open Source
SRT can be implemented using a free, open source code base, keeping costs low for all parties. There are no royalties, long-term contracts, or monthly subscription fees required. Being open source encourages SRT’s widespread adoption and accelerates innovation through continuous collaborative development. - Interoperability
With widespread adoption comes interoperability and longevity. Users can confidently deploy SRT through their entire video and audio streaming workflows knowing that multi-vendor products will work together seamlessly. - Cost-Effective
Thanks to SRT’s security and reliability, the public internet has now become a viable option for an expanded range of streaming applications. SRT offers significant operational flexibility and cost savings compared to satellite or custom network infrastructures.
“The benefits of SRT that we love to provide to our customer base include the visibility of where content is being distributed, the comfort of knowing that it’s secure, reliable, and performant, and the flexibility to ensure that we support a variety of different acquisition means.”
Peter Gibson, Executive Director of Product, Comcast Technology Solutions
How Does SRT Compare to Other Protocols?
SRT is most commonly compared to RTMP, a legacy protocol, which is still often used for video contribution. However, not only does SRT consistently outperform RTMP in terms of both latency and video quality, support for RTMP’s dated technology is dwindling. It’s a sentiment echoed by Deloitte in its recent report: Technology, Media, and Telecommunications Predictions 2020.
“Legacy protocols such as the real-time messaging protocol (RTMP), developed over a decade ago to encode video and move it across networks to clients, will likely be displaced by newer solutions such as secure reliable transport (SRT), designed to further decrease latency and meet the demands of live and on-demand streaming.”
Post time: Apr-28-2022

